
为SLAM3R补充实时处理函数方法
原本的SLAM3R的recon.py的处理顺序是一个offline的逻辑,将其添加了online处理的recon_online.py
在上个周阅读SLAM3R论文结束后,学长让我去看一下它的源代码 ↗,读完代码之后,发现虽然论文里讲述的是“可以实时重建”,但是实际上在recon.py文件中的scene_recon_pipeline函数中,代码采取了先对所有input_views进行输入到i2p_model得到res_feats,然后再将所有图片的token输入到l2w网络中进行重建的大致逻辑。
显然,这样的处理方法不是论文里所提出的online处理方法,因此,在过去的一个周里,本人一边练着科三 显然今天上午刚挂掉,该死的直线行驶😡 ,同时抽出了一点点时间完成了recon_online.py,一个把原本的scene_recon_pipeline改成online处理的改动。
原函数的处理逻辑#
阅读原函数的代码,我们可以将其分为以下几段:
预处理&得到所有view的token#
# Pre-save the RGB images along with their corresponding masks
# in preparation for visualization at last.
rgb_imgs = []
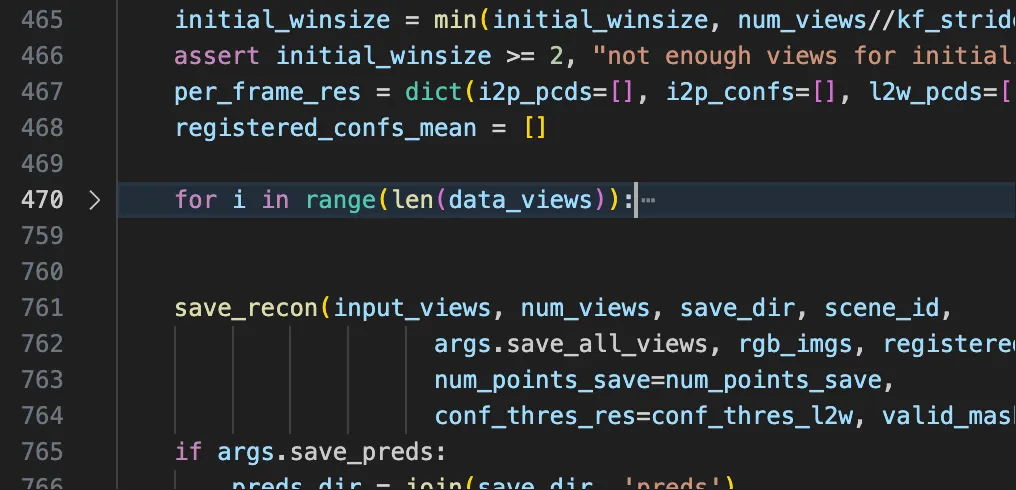
for i in range(len(data_views)):
if data_views[i]['img'].shape[0] == 1:
data_views[i]['img'] = data_views[i]['img'][0]
rgb_imgs.append(transform_img(dict(img=data_views[i]['img'][None]))[...,::-1])
if 'valid_mask' not in data_views[0]:
valid_masks = None
else:
valid_masks = [view['valid_mask'] for view in data_views]
#preprocess data for extracting their img tokens with encoder
for view in data_views:
view['img'] = torch.tensor(view['img'][None])
view['true_shape'] = torch.tensor(view['true_shape'][None])
for key in ['valid_mask', 'pts3d_cam', 'pts3d']:
if key in view:
del view[key]
to_device(view, device=args.device)
# pre-extract img tokens by encoder, which can be reused
# in the following inference by both i2p and l2w models
res_shapes, res_feats, res_poses = get_img_tokens(data_views, i2p_model) # 300+fps
print('finish pre-extracting img tokens')这里重点就是最后的res_shapes, res_feats, res_poses = get_img_tokens(data_views, i2p_model),采用i2p_model的_encode_multiview方法批次化地(batchify)对data_views进行处理,从而得到所有的view的token。
对所有view进行推理得到最合适的key_frame_stride#
这里的核心代码就是:
# decide the stride of sampling keyframes, as well as other related parameters
if args.keyframe_stride == -1:
kf_stride = adapt_keyframe_stride(input_views, i2p_model,
win_r = 3,
adapt_min=args.keyframe_adapt_min,
adapt_max=args.keyframe_adapt_max,
adapt_stride=args.keyframe_adapt_stride)
else:
kf_stride = args.keyframe_stride其中,adapt_keyframe_stride函数是一个典型的offline处理函数,它的功能是在所有的input_view中遍历可能的kf_stride取值,然后对每一个可能的取值随机取样,然后利用i2p_inference_batch函数得出置信度作为相似度?然后选取最高的所对应的kf_stride作为最优的取值。
使用初始的几个滑动窗口创建初始的全局scene&初始化buffer set#
因为SLAM3R初始化时的特殊性 ↗:
对于第一个帧这种特殊情况,我们采用了重复运行多次I2P获取足够多数量的初始帧作为缓冲集
在原本的offline格式的recon.py中,这种做法以这种样式呈现:
initial_pcds, initial_confs, init_ref_id = initialize_scene(input_views[:initial_winsize*kf_stride:kf_stride],
i2p_model,
winsize=initial_winsize,
return_ref_id=True) # 5*(1,224,224,3)
# start reconstrution of the whole scene
init_num = len(initial_pcds)
per_frame_res = dict(i2p_pcds=[], i2p_confs=[], l2w_pcds=[], l2w_confs=[])
for key in per_frame_res:
per_frame_res[key] = [None for _ in range(num_views)]
registered_confs_mean = [_ for _ in range(num_views)]
# set up the world coordinates with the initial window
for i in range(init_num):
per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][i*kf_stride] = initial_confs[i][0].to(args.device) # 224,224
registered_confs_mean[i*kf_stride] = per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][i*kf_stride].mean().cpu()
# initialize the buffering set with the initial window
assert args.buffer_size <= 0 or args.buffer_size >= init_num
buffering_set_ids = [i*kf_stride for i in range(init_num)]
# set up the world coordinates with frames in the initial window
for i in range(init_num):
input_views[i*kf_stride]['pts3d_world'] = initial_pcds[i]
initial_valid_masks = [conf > conf_thres_i2p for conf in initial_confs] # 1,224,224
normed_pts = normalize_views([view['pts3d_world'] for view in input_views[:init_num*kf_stride:kf_stride]],
initial_valid_masks)
for i in range(init_num):
input_views[i*kf_stride]['pts3d_world'] = normed_pts[i]
# filter out points with low confidence
input_views[i*kf_stride]['pts3d_world'][~initial_valid_masks[i]] = 0
per_frame_res['l2w_pcds'][i*kf_stride] = normed_pts[i] # 224,224,3其中,
initial_pcds, initial_confs, init_ref_id = initialize_scene(input_views[:initial_winsize*kf_stride:kf_stride],
i2p_model,
winsize=initial_winsize,
return_ref_id=True) # 5*(1,224,224,3)这一行是对初始化的几个view_token进行场景重建,并选出一开始的init_ref_id
然后之后就是把所有初始化的帧放到buffer_set里,然后进行一些归一化处理。
对原始的view再继续进行i2p重建点图#
这里我们重新遍历所有图像,对应论文里面通过I2P的decoder重建所有view的点图。此外,注意initial window的关键帧图片基本上已经在上面的初始化中被创建出了点图,因此我们选择略过他们,只对没有被创建点图的帧进行I2P处理
以得到点图,然后就采用论文中的输入窗口多个帧,重建每个帧的点云作为L2W model的输入。
for view_id in tqdm(range(num_views), desc="I2P resonstruction"):
# skip the views in the initial window
if view_id in buffering_set_ids:
# trick to mark the keyframe in the initial window
if view_id // kf_stride == init_ref_id:
per_frame_res['i2p_pcds'][view_id] = per_frame_res['l2w_pcds'][view_id].cpu()
else:
per_frame_res['i2p_pcds'][view_id] = torch.zeros_like(per_frame_res['l2w_pcds'][view_id], device="cpu")
per_frame_res['i2p_confs'][view_id] = per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][view_id].cpu()
continue
# construct the local window
sel_ids = [view_id]
for i in range(1,win_r+1):
if view_id-i*adj_distance >= 0:
sel_ids.append(view_id-i*adj_distance)
if view_id+i*adj_distance < num_views:
sel_ids.append(view_id+i*adj_distance)
local_views = [input_views[id] for id in sel_ids]
ref_id = 0
# recover points in the local window, and save the keyframe points and confs
output = i2p_inference_batch([local_views], i2p_model, ref_id=ref_id,
tocpu=False, unsqueeze=False)['preds']
#save results of the i2p model
per_frame_res['i2p_pcds'][view_id] = output[ref_id]['pts3d'].cpu() # 1,224,224,3
per_frame_res['i2p_confs'][view_id] = output[ref_id]['conf'][0].cpu() # 224,224
# construct the input for L2W model
input_views[view_id]['pts3d_cam'] = output[ref_id]['pts3d'] # 1,224,224,3
valid_mask = output[ref_id]['conf'] > conf_thres_i2p # 1,224,224
input_views[view_id]['pts3d_cam'] = normalize_views([input_views[view_id]['pts3d_cam']],
[valid_mask])[0]
input_views[view_id]['pts3d_cam'][~valid_mask] = 0 对初始窗口非关键帧进行注册#
显然我们在之前的初始化场景中只注册了关键帧,因此我们现在开始对非关键帧进行注册:
# Special treatment: register the frames within the range of initial window with L2W model
# TODO: batchify
if kf_stride > 1:
max_conf_mean = -1
for view_id in tqdm(range((init_num-1)*kf_stride), desc="pre-registering"):
if view_id % kf_stride == 0:
continue
# construct the input for L2W model
l2w_input_views = [input_views[view_id]] + [input_views[id] for id in buffering_set_ids]
# (for defination of ref_ids, see the doc of l2w_model)
output = l2w_inference(l2w_input_views, l2w_model,
ref_ids=list(range(1,len(l2w_input_views))),
device=args.device,
normalize=args.norm_input)
# process the output of L2W model
input_views[view_id]['pts3d_world'] = output[0]['pts3d_in_other_view'] # 1,224,224,3
conf_map = output[0]['conf'] # 1,224,224
per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][view_id] = conf_map[0] # 224,224
registered_confs_mean[view_id] = conf_map.mean().cpu()
per_frame_res['l2w_pcds'][view_id] = input_views[view_id]['pts3d_world']
if registered_confs_mean[view_id] > max_conf_mean:
max_conf_mean = registered_confs_mean[view_id]
print(f'finish aligning {(init_num-1)*kf_stride} head frames, with a max mean confidence of {max_conf_mean:.2f}')这里正如注释所说,是一个Special treatment。也是一个特殊情况处理。
缩放confs#
我们发现,我们只用l2w网络对非关键帧进行了置信度预测,关键帧的置信度是由之前的i2p网络进行预测的,作者在这里为了控制计算成本,选择直接将后者乘上一个常数因子进行缩放,大致反映出了场景的置信度分数:
# A problem is that the registered_confs_mean of the initial window is generated by I2P model,
# while the registered_confs_mean of the frames within the initial window is generated by L2W model,
# so there exists a gap. Here we try to align it.
max_initial_conf_mean = -1
for i in range(init_num):
if registered_confs_mean[i*kf_stride] > max_initial_conf_mean:
max_initial_conf_mean = registered_confs_mean[i*kf_stride]
factor = max_conf_mean/max_initial_conf_mean
# print(f'align register confidence with a factor {factor}')
for i in range(init_num):
per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][i*kf_stride] *= factor
registered_confs_mean[i*kf_stride] = per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][i*kf_stride].mean().cpu()对剩下的views进行注册#
OK,经过了以上的对于初始帧的特殊处理,我们终于踏入了正途:在过程中对每个帧进行实时处理
从buffer set里选择最相近的sel_num个帧:#
# select sccene frames in the buffering set to work as a global reference
cand_ref_ids = buffering_set_ids
ref_views, sel_pool_ids = scene_frame_retrieve(
[input_views[i] for i in cand_ref_ids],
input_views[ni:ni+num_register:2],
i2p_model, sel_num=num_scene_frame,
# cand_recon_confs=[per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][i] for i in cand_ref_ids],
depth=2)这里正如论文中所述,采用了i2p_model的前2个decoder进行相似评分。
将选取的最相近的几个帧作为参考合并当前帧进行l2w重建#
显而易见,言以概之:
# register the source frames in the local coordinates to the world coordinates with L2W model
l2w_input_views = ref_views + input_views[ni:max_id+1]
input_view_num = len(ref_views) + max_id - ni + 1
assert input_view_num == len(l2w_input_views)
output = l2w_inference(l2w_input_views, l2w_model,
ref_ids=list(range(len(ref_views))),
device=args.device,
normalize=args.norm_input)
# process the output of L2W model
src_ids_local = [id+len(ref_views) for id in range(max_id-ni+1)] # the ids of src views in the local window
src_ids_global = [id for id in range(ni, max_id+1)] #the ids of src views in the whole dataset
succ_num = 0
for id in range(len(src_ids_global)):
output_id = src_ids_local[id] # the id of the output in the output list
view_id = src_ids_global[id] # the id of the view in all views
conf_map = output[output_id]['conf'] # 1,224,224
input_views[view_id]['pts3d_world'] = output[output_id]['pts3d_in_other_view'] # 1,224,224,3
per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][view_id] = conf_map[0]
registered_confs_mean[view_id] = conf_map[0].mean().cpu()
per_frame_res['l2w_pcds'][view_id] = input_views[view_id]['pts3d_world']
succ_num += 1通过一些手段更新buffer set#
buffer_set的选取方法差不多就和论文里面讲的一样,基本上就是随机选取了。
# update the buffering set
if next_register_id - milestone >= update_buffer_intv:
while(next_register_id - milestone >= kf_stride):
candi_frame_id += 1
full_flag = max_buffer_size > 0 and len(buffering_set_ids) >= max_buffer_size
insert_flag = (not full_flag) or ((strategy == 'fifo') or
(strategy == 'reservoir' and np.random.rand() < max_buffer_size/candi_frame_id))
if not insert_flag:
milestone += kf_stride
continue
# Use offest to ensure the selected view is not too close to the last selected view
# If the last selected view is 0,
# the next selected view should be at least kf_stride*3//4 frames away
start_ids_offset = max(0, buffering_set_ids[-1]+kf_stride*3//4 - milestone)
# get the mean confidence of the candidate views
mean_cand_recon_confs = torch.stack([registered_confs_mean[i]
for i in range(milestone+start_ids_offset, milestone+kf_stride)])
mean_cand_local_confs = torch.stack([local_confs_mean[i]
for i in range(milestone+start_ids_offset, milestone+kf_stride)])
# normalize the confidence to [0,1], to avoid overconfidence
mean_cand_recon_confs = (mean_cand_recon_confs - 1)/mean_cand_recon_confs # transform to sigmoid
mean_cand_local_confs = (mean_cand_local_confs - 1)/mean_cand_local_confs
# the final confidence is the product of the two kinds of confidences
mean_cand_confs = mean_cand_recon_confs*mean_cand_local_confs
most_conf_id = mean_cand_confs.argmax().item()
most_conf_id += start_ids_offset
id_to_buffer = milestone + most_conf_id
buffering_set_ids.append(id_to_buffer)
# print(f"add ref view {id_to_buffer}")
# since we have inserted a new frame, overflow must happen when full_flag is True
if full_flag:
if strategy == 'reservoir':
buffering_set_ids.pop(np.random.randint(max_buffer_size))
elif strategy == 'fifo':
buffering_set_ids.pop(0)
# print(next_register_id, buffering_set_ids)
milestone += kf_stride
# transfer the data to cpu if it is not in the buffering set, to save gpu memory
for i in range(next_register_id):
to_device(input_views[i], device=args.device if i in buffering_set_ids else 'cpu')保存环节#
当我们处理完所有帧后,我们会保存我们的所有帧的点云,把这些所有帧的点云合到一起进行重建,得出最后的场景点云。
review#
显而易见,原recon.py中的这个pipeline是一个完全的offline处理方法,因此,我编写了一个真正的(?online版本的方法,处理逻辑如下所示:
online 函数的处理逻辑#
既然是要online,我们显然第一件要做的事情就是写下:
for i in range(len(data_views)):之后我们在进行一系列处理:
预处理 & 得到当前view的token#
显然,通过对原先offline版本的函数分析,这个过程没有初始化的困扰,因此,我们可以大胆对所有遍历到的view都进行这一步:
# Pre-save the RGB images along with their corresponding masks
# in preparation for visualization at last.
if data_views[i]['img'].shape[0] == 1:
data_views[i]['img'] = data_views[i]['img'][0]
rgb_imgs.append(transform_img(dict(img=data_views[i]['img'][None]))[...,::-1])
if is_have_mask_rgb:
valid_masks.append(data_views[i]['valid_mask'])
# process now image for extracting its img token with encoder
data_views[i]['img'] = torch.tensor(data_views[i]['img'][None])
data_views[i]['true_shape'] = torch.tensor(data_views[i]['true_shape'][None])
for key in ['valid_mask', 'pts3d_cam', 'pts3d']:
if key in data_views[i]:
del data_views[key]
to_device(data_views[i], device=args.device)
# pre-extract img tokens by encoder, which can be reused
# in the following inference by both i2p and l2w models
temp_shape, temp_feat, temp_pose = get_single_img_tokens([data_views[i]], i2p_model, True)
res_shapes.append(temp_shape[0])
res_feats.append(temp_feat[0])
res_poses.append(temp_pose[0])
print(f"finish pre-extracting img token of view {i}")
input_views.append(dict(label=data_views[i]['label'],
img_tokens=temp_feat[0],
true_shape=data_views[i]['true_shape'],
img_pos=temp_pose[0]))
for key in per_frame_res:
per_frame_res[key].append(None)
registered_confs_mean.append(i)这里我使用了一个get_single_img_tokens函数,与之前的get_img_tokens函数相比,该函数除了不能batch化(online的限制)之外,效果输出别无二致。
积累帧以用于场景初始化#
需要注意的是,当帧序数小于初始化所需要的帧数时,我们后续的程序均无法进行,因此在我的代码中,我选择直接跳过,先蓄势待发🤣
一旦积累到初始化场景所需帧后,函数会采用一系列操作初始化场景以及初始化buffer set,对初始化后的各帧点云进行归一化处理:
# accumulate the initial window frames
if i < (initial_winsize - 1)*kf_stride and i % kf_stride == 0:
continue
elif i == (initial_winsize - 1)*kf_stride:
initial_pcds, initial_confs, init_ref_id = initialize_scene(input_views[:initial_winsize*kf_stride:kf_stride],
i2p_model,
winsize=initial_winsize,
return_ref_id=True)
# set up the world coordinates with the initial window
init_num = len(initial_pcds)
for j in range(init_num):
per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][j * kf_stride] = initial_confs[j][0].to(args.device)
registered_confs_mean[j * kf_stride] = per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][j * kf_stride].mean().cpu()
# initialize the buffering set with the initial window
assert args.buffer_size <= 0 or args.buffer_size >= init_num
buffering_set_ids = [j*kf_stride for j in range(init_num)]
# set ip the woeld coordinates with frames in the initial window
for j in range(init_num):
input_views[j*kf_stride]['pts3d_world'] = initial_pcds[j]
initial_valid_masks = [conf > conf_thres_i2p for conf in initial_confs]
normed_pts = normalize_views([view['pts3d_world'] for view in input_views[:init_num*kf_stride:kf_stride]],
initial_valid_masks)
for j in range(init_num):
input_views[j*kf_stride]['pts3d_world'] = normed_pts[j]
# filter out points with low confidence
input_views[j*kf_stride]['pts3d_world'][~initial_valid_masks[j]] = 0
per_frame_res['l2w_pcds'][j*kf_stride] = normed_pts[j]
elif i < (initial_winsize - 1) * kf_stride:
continue需要注意的是,这里一旦积累到足够多的初始帧,我们就不会进行continue处理了,然后直接进行下一部分。
对之前积累的view进行i2p重建点图(包含正在处理的帧) & 注册初始窗口非关键帧#
这里我们采用类似于之前offline的顺序,只不过把外在的表现形式作出了改变,实际上内在的顺序逻辑基本不变:
# first recover the accumulate views
if i == (initial_winsize - 1) * kf_stride:
for view_id in range(i + 1):
# skip the views in the initial window
if view_id in buffering_set_ids:
# trick to mark the keyframe in the initial window
if view_id // kf_stride == init_ref_id:
per_frame_res['i2p_pcds'][view_id] = per_frame_res['l2w_pcds'][view_id].cpu()
else:
per_frame_res['i2p_pcds'][view_id] = torch.zeros_like(per_frame_res['l2w_pcds'][view_id], device="cpu")
per_frame_res['i2p_confs'][view_id] = per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][view_id].cpu()
print(f"finish revocer pcd of frame {view_id} in their local coordinates(in buffer set), with a mean confidence of {per_frame_res['i2p_confs'][view_id].mean():.2f} up to now.")
continue
# construct the local window with the initial views
sel_ids = [view_id]
for j in range(1, win_r + 1):
if view_id - j * adj_distance >= 0:
sel_ids.append(view_id - j * adj_distance)
if view_id + j * adj_distance < i:
sel_ids.append(view_id + j * adj_distance)
local_views = [input_views[id] for id in sel_ids]
ref_id = 0
# recover poionts in the initial window, and save the keyframe points and confs
output = i2p_inference_batch([local_views], i2p_model, ref_id=ref_id,
tocpu=False, unsqueeze=False)['preds']
# save results of the i2p model for the initial window
per_frame_res['i2p_pcds'][view_id] = output[ref_id]['pts3d'].cpu()
per_frame_res['i2p_confs'][view_id] = output[ref_id]['conf'][0].cpu()
# construct the input for L2W model
input_views[view_id]['pts3d_cam'] = output[ref_id]['pts3d']
valid_mask = output[ref_id]['conf'] > conf_thres_i2p
input_views[view_id]['pts3d_cam'] = normalize_views([input_views[view_id]['pts3d_cam']],
[valid_mask])[0]
input_views[view_id]['pts3d_cam'][~valid_mask] = 0
local_confs_mean_up2now = [conf.mean() for conf in per_frame_res['i2p_confs'] if conf is not None]
print(f"finish revocer pcd of frame {view_id} in their local coordinates, with a mean confidence of {torch.stack(local_confs_mean_up2now).mean():.2f} up to now.")
# Special treatment: register the frames within the range of initial window with L2W model
if kf_stride > 1:
max_conf_mean = -1
for view_id in tqdm(range((init_num - 1) * kf_stride), desc="pre-registering"):
if view_id % kf_stride == 0:
continue
# construct the input for L2W model
l2w_input_views = [input_views[view_id]] + [input_views[id] for id in buffering_set_ids]
# (for defination of ref_ids, seee the doc of l2w_model)
output = l2w_inference(l2w_input_views, l2w_model,
ref_ids=list(range(1,len(l2w_input_views))),
device=args.device,
normalize=args.norm_input)
# process the output of L2W model
input_views[view_id]['pts3d_world'] = output[0]['pts3d_in_other_view'] # 1,224,224,3
conf_map = output[0]['conf'] # 1,224,224
per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][view_id] = conf_map[0] # 224,224
registered_confs_mean[view_id] = conf_map.mean().cpu()
per_frame_res['l2w_pcds'][view_id] = input_views[view_id]['pts3d_world']
if registered_confs_mean[view_id] > max_conf_mean:
max_conf_mean = registered_confs_mean[view_id]
print(f'finish aligning {(init_num)*kf_stride} head frames, with a max mean confidence of {max_conf_mean:.2f}')
# A problem is that the registered_confs_mean of the initial window is generated by I2P model,
# while the registered_confs_mean of the frames within the initial window is generated by L2W model,
# so there exists a gap. Here we try to align it.
max_initial_conf_mean = -1
for i in range(init_num):
if registered_confs_mean[i*kf_stride] > max_initial_conf_mean:
max_initial_conf_mean = registered_confs_mean[i*kf_stride]
factor = max_conf_mean/max_initial_conf_mean
# print(f'align register confidence with a factor {factor}')
for i in range(init_num):
per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][i*kf_stride] *= factor
registered_confs_mean[i*kf_stride] = per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][i*kf_stride].mean().cpu()
# register the rest frames with L2W model
next_register_id = (init_num - 1) * kf_stride + 1
milestone = init_num * kf_stride + 1
update_buffer_intv = kf_stride*args.update_buffer_intv # update the buffering set every update_buffer_intv frames
max_buffer_size = args.buffer_size
strategy = args.buffer_strategy
candi_frame_id = len(buffering_set_ids) # used for the reservoir sampling strategy
continue然后在处理完这么一堆之后我们直接continue到下一个循环。
处理新图片#
在下一个循环中,我们拿到了新图片,此时我们也在我们的online函数中踏上了正途,可以对每一个帧进行实时处理了。
这里,我们的处理逻辑与第一种方法类似,不同的一点是我是一帧一帧地去处理。
保存环节#
与上一个方法略微不同,我提供了参数选项选择是否在线保存/逐几帧保存,因此我重写了一个增量式保存的类:
class IncrementalReconstructor:
"""
A class used for reconstruting the pts incrementally
"""
def __init__(self):
self.res_pcds = None
self.res_rgbs = None
self.res_confs = None
self.res_valid_masks = None
self.is_initialized = False
def add_frame(self, view: dict, img: np.ndarray, conf: np.ndarray = None, valid_mask: np.ndarray = None):
"""
Incrementally add a new frame of view data.
Args:
view (dict): a dictionary for a new view
img (np.ndarray): rgb_img
conf (np.ndarray, optional):
valid_mask (np.ndarray, optional):
"""
try:
new_pcd = to_numpy(view['pts3d_world']).reshape(-1, 3)
new_rgb = to_numpy(img).reshape(-1, 3)
except KeyError:
print(f"Warning: 'pts3d_world' not found in the new view. Frame skipped.")
return
if not self.is_initialized:
self.res_pcds = new_pcd
self.res_rgbs = new_rgb
if conf is not None:
self.res_confs = to_numpy(conf).reshape(-1)
if valid_mask is not None:
self.res_valid_masks = to_numpy(valid_mask).reshape(-1)
self.is_initialized = True
else:
self.res_pcds = np.concatenate([self.res_pcds, new_pcd], axis=0)
self.res_rgbs = np.concatenate([self.res_rgbs, new_rgb], axis=0)
if conf is not None:
new_conf = to_numpy(conf).reshape(-1)
self.res_confs = np.concatenate([self.res_confs, new_conf], axis=0)
if valid_mask is not None:
new_mask = to_numpy(valid_mask).reshape(-1)
self.res_valid_masks = np.concatenate([self.res_valid_masks, new_mask], axis=0)
def save_snapshot(self, snapshot_id: int, save_dir: str, num_points_save: int = 200000, conf_thres_res: float = 3.0):
"""
Just save
"""
if not self.is_initialized:
print("Warning: Reconstructor not initialized. Nothing to save.")
return
save_name = f"recon_snapshot_{snapshot_id:05d}.ply"
pts_count = len(self.res_pcds)
final_valid_mask = np.ones(pts_count, dtype=bool)
if self.res_valid_masks is not None:
final_valid_mask &= self.res_valid_masks
if self.res_confs is not None:
conf_masks = self.res_confs > conf_thres_res
final_valid_mask &= conf_masks
valid_ids = np.where(final_valid_mask)[0]
if len(valid_ids) == 0:
print(f"Warning for snapshot {snapshot_id}: No valid points left after filtering.")
return
print(f'Snapshot {snapshot_id}: Ratio of points filtered out: {(1. - len(valid_ids) / pts_count) * 100:.2f}%')
n_samples = min(num_points_save, len(valid_ids))
print(f"Snapshot {snapshot_id}: Resampling {n_samples} points from {len(valid_ids)} valid points.")
sampled_idx = np.random.choice(valid_ids, n_samples, replace=False)
sampled_pts = self.res_pcds[sampled_idx]
sampled_rgbs = self.res_rgbs[sampled_idx]
save_path = join(save_dir, save_name)
print(f"Saving reconstruction snapshot to {save_path}")
save_ply(points=sampled_pts, save_path=save_path, colors=sampled_rgbs)在每一个循环最后加以调用:
reconstructor.add_frame(
view=input_views[i],
img=rgb_imgs[i],
conf=per_frame_res['l2w_confs'][i],
valid_mask=valid_masks
)
if args.save_online:
if (i + 1) % args.save_frequency == 0:
reconstructor.save_snapshot(
snapshot_id=i + 1,
save_dir=save_dir,
num_points_save=num_points_save,
conf_thres_res=conf_thres_l2w
)OK,到此为止我就写完了原本的处理逻辑的解释和新写的**onlinee*处理逻辑介绍,其实要说不说,online处理逻辑也并非太过复杂,但是奈何我这几天因为学车耽误了太多时间也没做什么东西(x
又水了一篇blog😋新的仓库:#
Waiting for api.github.com...